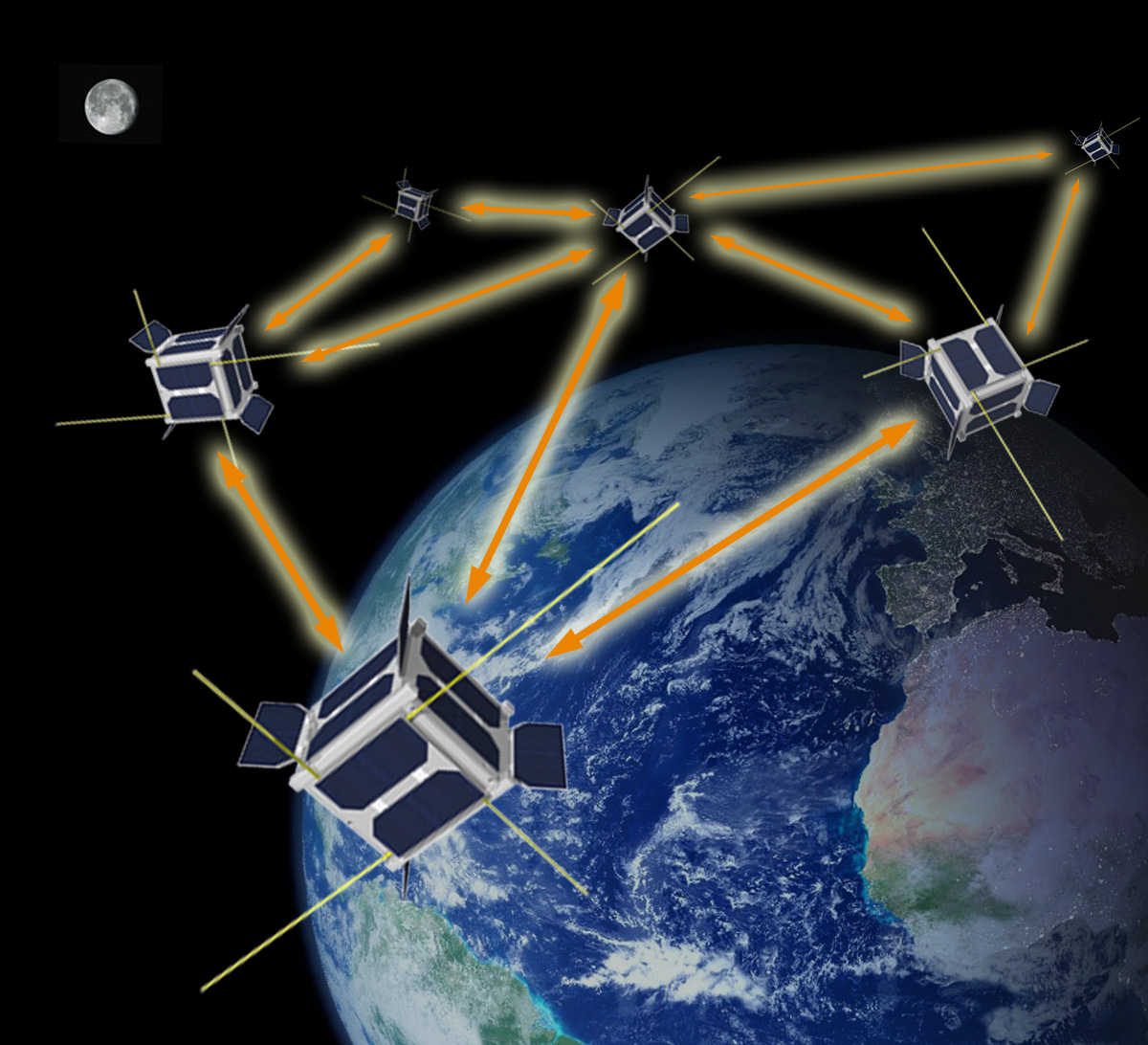
PIPP OLFAR: Breakthrough technologies for Interferometry in Space
Publications
- Frequency augumented clock synchronizaion for space-based interferometry
Felix Abel; Prem Sundaramoorthy; Raj Thilak Rajan;
In Small Satellite Systems and Services : 4S Symposium,
ESA/ESTEC, pp. 14, May 2022.
document - Applications and Potentials of Intelligent Swarms for magnetospheric studies
Raj Thilak Rajan; Shoshana Ben-Maor; Shaziana Kaderali; Calum Turner; Mohammed Milhim; Catrina Melograna; Dawn Haken; Gary Paul; Vedant; V. Sreekumar; Johannes Weppler; Yosephine Gumulya; Riccardo Bunt; Asia Bulgarini; Maurice Marnat; Kadri Bussov; Frederick Pringle; Jusha Ma; Rushanka Amrutkar; Miguel Coto; Jiang He; Zijian Shi; Shahd Hayder; Dina Saad Fayez Jaber; Junchao Zuo; Mohammad Alsukour; Cécile Renaud; Matthew Chris;
Acta Astronautica,
2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2021.07.046
Keywords: ...
Satellite swarms, Intelligent swarms, Heliophysics, Magnetosphere, Cubesats, Next generation space systems.
Abstract: ...
Earth’s magnetosphere is vital for today’s technologically dependent society. To date, numerous design studies have been conducted and over a dozen science missions have flown to study the magnetosphere. However, a majority of these solutions relied on large monolithic satellites, which limited the spatial resolution of these investigations, as did the technological limitations of the past. To counter these limitations, we propose the use of a satellite swarm carrying numerous and distributed payloads for magnetospheric measurements. Our mission is named APIS — Applications and Potentials of Intelligent Swarms. The APIS mission aims to characterize fundamental plasma processes in the Earth’s magnetosphere and measure the effect of the solar wind on our magnetosphere. We propose a swarm of 40 CubeSats in two highly-elliptical orbits around the Earth, which perform radio tomography in the magnetotail at 8–12 Earth Radii (RE) downstream, and the subsolar magnetosphere at 8–12 RE upstream. These maps will be made at both low-resolutions (at 0.5 RE, 5 s cadence) and high-resolutions (at 0.025 RE, 2 s cadence). In addition, in-situ measurements of the magnetic and electric fields, plasma density will be performed by on-board instruments. In this article, we present an outline of previous missions and designs for magnetospheric studies, along with the science drivers and motivation for the APIS mission. Furthermore, preliminary design results are included to show the feasibility of such a mission. The science requirements drive the APIS mission design, the mission operation and the system requirements. In addition to the various science payloads, critical subsystems of the satellites are investigated e.g., navigation, communication, processing and power systems. Our preliminary investigation on the mass, power and link budgets indicate that the mission could be realized using Commercial Off-the-Shelf (COTS) technologies and with homogeneous CubeSats, each with a 12U form factor. We summarize our findings, along with the potential next steps to strengthen our design study.
document - Simulated Megaconstellation Ephemerides
Calum Turner; Raj ThilakRajan;
Technical report, July 2021. DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.21227/s1qk-xt91
Abstract: ...
Time-varying positions, velocities, and orbital elements of 1584 satellites in a simulated megaconstellation modelled on Phase 1 of SpaceX’s Starlink. This technical note accompanies a dataset providing the time-varying positions of 1584 satellites in a simulated megaconstellation modelled on Phase 1 of SpaceX’s Starlink. This note explains the context, creation, format, and potential uses of the dataset. The code used to create these data is publicly available
document - A roadmap towards a space-based radio telescope for ultra-low frequency radio astronomy
M.J. Bentum; M.K. Verma; R.T. Rajan; A.J. Boonstra; C.J.M. Verhoeven; E.K.A. Gill; A.J. {van der Veen}; H. Falcke; M. Klein Wolt; B. Monna; S. Engelen; J. Rotteveel; L.I. Gurvits;
Advances in Space Research,
Volume 65, Issue 2, pp. 856-867, 2020. High-resolution space-borne radio astronomy. DOI: 10.1016/j.asr.2019.09.007
document - Lunar Orbit Design of a Satellite Swarm for Radio Astronomy
Mok, Sung-Hoon; Guo, Jian; Gill, Eberhard; Rajan, Raj Thilak;
In 2020 IEEE Aerospace Conference,
pp. 1-9, 2020. DOI: 10.1109/AERO47225.2020.9172468 - Autonomous Mission Planning for OLFAR: A Satellite Swarm in Lunar Orbit for Radio Astronomy
Mok, S; Guo, J; Gill, EKA; Rajan, RT;
In 71st International Astronautical Congress (IAC),
IAF/AIAA, 2020.
document - APIS: Applications and Potentials of Intelligent Swarms for magnetospheric studies
R.T. Rajan; S. Ben-Maor; S. Kaderali; Others;
In 71th International Astronautical Congress (IAC),
2020.
document - End-of-life of satellite swarms
Turner, Calum; Raj Thilak Rajan;
In 71st International Astronautical Congress (IAC),
IAF/AIAA, 2020.
document - Relative kinematics of an anchorless network
R. T. Rajan; G. Leus; A.J. van der Veen;
Signal Processing,
Volume 157, pp. 266-279, April 2019. ISSN: 0165-1684. DOI: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2018.11.005
document - Low-frequency observations using high-altitude balloon experiments (LOBE)
Raj Thilak Rajan; P.Sundaramoorthy; C.J.C.Vertegaal; A.Montagne; V.Karunanithi; M.K.Verma; M.Bentum; C.Verhoeven;
In 70th International Astronautical Congress (IAC),
IAF, October 2019.
document - High Data-Rate Inter-Satellite Link (ISL) For Space-Based Interferometry
Visweswaran Karunanithi; Raj Thilak Rajan; P.Sundaramoorthy; M.K.Verma; C.Verhoeven; M. Bentum; E.W. McCune;
In 70th International Astronautical Congress (IAC),
IAF, October 2019.
document - A Low-Power CMOS Low Noise Amplifier for Space-based Low-frequency Radio Astronomy
S.Babayan-Mashhadi; R.T.Rajan; M.Bentum; C.Verhoeven;
In 70th International Astronautical Congress (IAC),
IAF, October 2019.
document
BibTeX support